China Maps
| India Facts | India Flag | India Pics |
GK NXT - Great Knowledge for Genius Kids
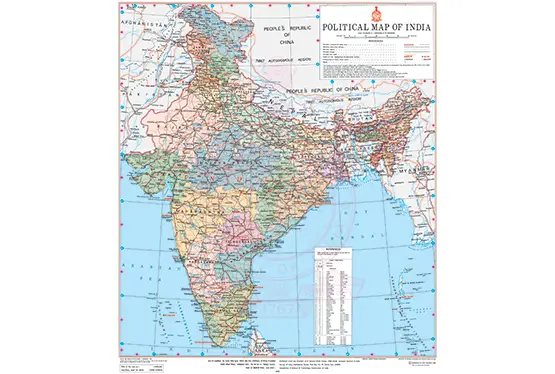
The map of China is a testament to one of the world’s oldest civilizations and its evolution through millennia. Spanning over 9.6 million square kilometers, China is the third-largest country globally, boasting diverse topography, cultural heritage, and historical significance. From the towering Himalayas to the fertile plains of the Yangtze River, China’s map narrates a story of natural wealth and human ingenuity.
China’s geography is as varied as its rich history. It borders 14 countries, including Russia, India, and Vietnam, and features an extensive coastline along the East and South China Seas. Its terrain includes mountains, plateaus, deserts, rivers, and plains, making it one of the most geographically diverse countries in the world.
The key geographical regions of China include:
- The Tibetan Plateau: Known as the "Roof of the World," this region is home to Mount Everest, the world’s highest peak, standing at 8,848 meters.
- The Northern Plains: Including the Yellow River basin, this region has historically been the cradle of Chinese civilization.
- The Southern Hills: Renowned for their karst landscapes, these hills include the famous Guilin region.
- The Gobi Desert: Shared with Mongolia, this desert is a stark yet stunning expanse of arid land.
China’s map has evolved significantly over centuries, shaped by dynasties, wars, and trade. The Silk Road, an ancient trade route linking China to Europe, was instrumental in fostering cultural and economic exchanges. The Great Wall, visible on maps, is a marvel of ancient engineering that underscores the importance of defense in Chinese history.
In modern history, regions like Hong Kong and Macau, marked on the map, reflect colonial influences and their eventual return to Chinese sovereignty. The demarcation of boundaries in Tibet and Xinjiang highlights the complex interplay between geography and politics.
China’s map is also a reflection of its cultural diversity. With 56 recognized ethnic groups, the country is a mosaic of languages, traditions, and cuisines. The Han Chinese make up the majority, but regions like Xinjiang and Inner Mongolia are home to distinct ethnic communities such as the Uyghurs and Mongols.
Each region contributes uniquely to China’s cultural tapestry. Sichuan is known for its fiery cuisine, while Tibet boasts a rich tradition of Buddhist art and architecture. The Yangtze River Delta, marked by cities like Shanghai, showcases China’s modernity and historical depth.
The map of China highlights numerous natural wonders that attract global admiration. The Zhangjiajie National Forest Park, with its towering sandstone pillars, inspired the landscapes in the movie "Avatar." The Li River, flowing through Guilin, is celebrated for its picturesque scenery that has inspired countless artists.
China is also home to diverse ecosystems, from the tropical rainforests of Yunnan to the icy expanses of Heilongjiang. These areas are crucial for biodiversity, hosting species like the giant panda and the snow leopard.
Politically, China is divided into 23 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 municipalities, and 2 Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). This division is essential for governance, as regions like Tibet and Xinjiang have unique administrative arrangements.
Economically, the map showcases key hubs like the Pearl River Delta, a powerhouse of manufacturing and trade, and the Bohai Economic Rim, centered around Beijing and Tianjin. The Belt and Road Initiative, a modern reimagining of the Silk Road, further emphasizes China’s geopolitical strategy.
China’s map is a treasure trove for travelers. Iconic destinations include the Forbidden City in Beijing, the Terracotta Army in Xi’an, and the serene West Lake in Hangzhou. Modern cities like Shanghai blend skyscrapers with colonial architecture, offering a glimpse into China’s dynamic evolution.
The high-speed rail network, spanning over 40,000 kilometers, makes navigating China’s vast landscape efficient and accessible, connecting tourists to both metropolitan centers and remote wonders.
FAQ
Q: What is the size of China?
A: China spans approximately 9.6 million square kilometers, making it the third-largest country in the world.
Q: What are some key natural features of China?
A: Key natural features include the Tibetan Plateau, the Gobi Desert, the Yangtze River, and Zhangjiajie National Forest Park.
Q: How is China administratively divided?
A: China is divided into 23 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 municipalities, and 2 Special Administrative Regions.
Q: What are China’s major economic hubs?
A: Major economic hubs include the Pearl River Delta, the Yangtze River Delta, and the Bohai Economic Rim.
The map of China is more than a geographic representation; it is a narrative of a nation’s history, culture, and aspirations. From ancient trade routes to modern megacities, and from breathtaking natural wonders to profound cultural legacies, China’s map encapsulates a story of resilience, diversity, and innovation. Whether studied academically or explored as a travel guide, the map of China continues to captivate and educate.